
This website does not provide cost information. To locate a medical imaging or radiation oncology provider in your community, you can search the ACR-accredited facilities database. Please contact your physician with specific medical questions or for a referral to a radiologist or other physician. Image guidance, including fluoroscopy, x-ray, ultrasound or CT, is used.Įach of these tests will help your doctor further evaluate your lungs and lung function or help determine the type of germ causing your pneumonia. If an abscess has formed in the lungs, it may be drained by inserting a small drainage tube (catheter). Image-guided abscess drainage : Image-guidance helps direct placement of a needle into the abscess cavity and can aid during insertion of a drainage tube.The procedure is performed under the guidance of CT or ultrasound. The tube can help remove excess fluid or air. Chest tube placement : During this procedure, also known as thoracostomy, a thin plastic tube is inserted into the pleural space (the area between the chest wall and lungs.The fluid removed during this procedure may also help provide symptom relief. X-ray, CT and/or ultrasound may be used during thoracentesis. Thoracentesis : Fluid may be taken from your chest cavity and studied to help your doctor determine which germ is causing your illness.The following image-guided treatments may be used for pneumonia: Biopsies of the lung can be done using x-ray, CT, ultrasound and/or MRI. This procedure involves removing several small samples from your lung(s) and examining them. Needle biopsy of the lung : Your doctor may request a biopsy of your lung(s) to determine the cause of pneumonia.If the lungs are abnormal because of excess fluid, infection or tumor, an MRI may provide additional information about the cause or extent of these abnormalities. MRI of the chest : MRI is not generally used to evaluate for pneumonia but may be used to look at the heart, vessels of the chest and chest wall structures.An ultrasound exam will help determine how much fluid is present and can aid in determining the cause of the fluid. Ultrasound of the chest : Ultrasound may be used if fluid surrounding the lungs is suspected.A CT scan can also show complications of pneumonia, abscesses or pleural effusions and enlarged lymph nodes. A CT scan also shows the airway (trachea and bronchi) in great detail and can help determine if pneumonia may be related to a problem within the airway.

CT of the lungs : A CT scan of the chest may be done to see finer details within the lungs and detect pneumonia that may be more difficult to see on a plain x-ray.

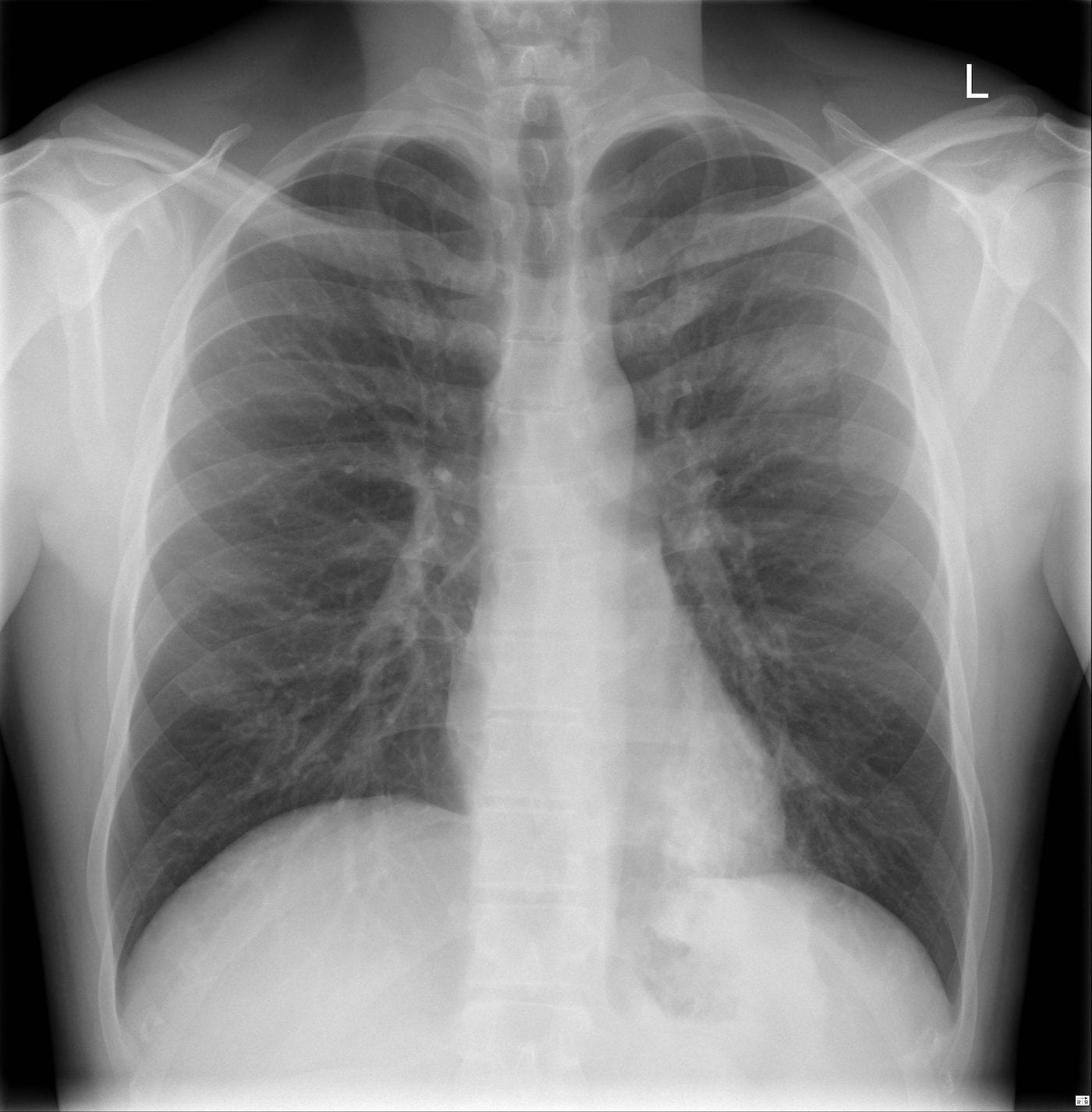
This exam will also help determine if you have any complications related to pneumonia such as abscesses or pleural effusions (fluid surrounding the lungs). When interpreting the x-ray, the radiologist will look for white spots in the lungs (called infiltrates) that identify an infection.

You will also undergo a physical exam, so that your doctor can listen to your lungs. Your primary doctor will begin by asking you about your medical history and symptoms. How is pneumonia diagnosed and evaluated?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
